| [1]Lehman RA Jr, Lenke LG, Keeler KA, et al. Operative treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis with posterior pedicle screw-only constructs: minimum three-year follow-up of one hundred fourteen cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33(14):1598-1604. [2]杨立利,陈华江,陈德玉,等.计算机辅助导航技术在脊柱侧凸术中应用的初步经验[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(23):1773- 1776.[3]陈立言,彭新生,李佛保,等.椎弓根钉固定在10岁以下小儿胸腰椎疾患治疗中的应用[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,16(4):263-266.[4]董健文,戎利民,刘斌,等.胸椎椎弓根外固定技术的临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(44):8697-8700.[5]Maruyama T, Takeshita K, Nakamura K, et al. Spatial relations between the vertebral body and the thoracic aorta in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29(18):2067-2069.[6]崔新刚,张佐伦,陈海松,等.胸椎椎弓根根外内固定的应用解剖学研究及其意义[J].中华创伤杂志,2005,21(10):768-772.[7]McCormack BM, Benzel EC, Adams MS, et al. Anatomy of the thoracic pedicle. Neurosurgery. 1995;37(2):303-308.[8]邢文华,贾连顺,霍洪军,等.胸椎椎弓根-肋骨复合体螺钉置入内固定的应用解剖学特征[J].中国组织工程与临床康复,2011, 15(43):8063-8067.[9]谢陶敢,陈其昕,李方才,等.胸椎椎弓根-肋骨单元与椎弓根的CT测量[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2008,18(9):665-668.[10]Dvorak M, MacDonald S, Gurr KR, et al. An anatomic, radiographic, and biomechanical assessment of extrapedicular screw fixation in the thoracic spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(12):1689-1694.[11]O'Brien MF, Lenke LG, Mardjetko S, et al. Pedicle morphology in thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: is pedicle fixation an anatomically viable technique? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(18):2285-2293.[12]Kim YJ, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, et al. Free hand pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine: is it safe? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(3):333-342.[13]Krag MH, Beynnon BD, Pope MH, et al. Depth of insertion of transpedicular vertebral screws into human vertebrae: effect upon screw-vertebra interface strength. J Spinal Disord. 1988; 1(4):287-294.[14]Okuyama K, Sato K, Abe E, et al. Stability of transpedicle screwing for the osteoporotic spine. An in vitro study of the mechanical stability. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(15): 2240-2245.[15]Husted DS, Haims AH, Fairchild TA, et al. Morphometric comparison of the pedicle rib unit to pedicles in the thoracic spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(2):139-146.[16]韦兴,侯树勋,史亚民,等.胸椎经“椎弓根-肋骨间”螺钉与椎弓根螺钉固定的抗拔出力比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006;16(8): 623-625.[17]Ebraheim NA, Jabaly G, Xu R, et al. Anatomic relations of the thoracic pedicle to the adjacent neural structures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997;22(14):1553-1557.[18]吴叶,侯树勋,吴闻文,等.胸椎椎弓根螺钉植入位置的分区及临床意义[J].中华外科杂志,2005,43(24):1572-1575.[19]Guzey FK, Emel E, Hakan Seyithanoglu M, et al. Accuracy of pedicle screw placement for upper and middle thoracic pathologies without coronal plane spinal deformity using conventional methods. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2006;19(6): 436-441.[20]Bhandari M, Patenall V, Devereaux PJ, et al. An observational study of duplicate presentation rates between two national orthopedic meetings. Can J Surg. 2005;48(2):117-122.[21]Deligianni D, Korovessis P, Baikousis A, et al. Factor analysis of the effectiveness of transfixation and rod characteristics on the TSRH screw-rod instrumentation. J Spinal Disord. 2000; 13(1):50-57.[22]Hasegawa K, Takahashi HE, Uchiyama S, et al. An experimental study of a combination method using a pedicle screw and laminar hook for the osteoporotic spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997;22(9):958-963.[23]Zdeblick TA, Kunz DN, Cooke ME, et al. Pedicle screw pullout strength. Correlation with insertional torque. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(12):1673-1676.[24]White KK, Oka R, Mahar AT, et al. Pullout strength of thoracic pedicle screw instrumentation: comparison of the transpedicular and extrapedicular techniques. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(12):E355-358.[25]Krag MH, Beynnon BD, Pope MH, et al. Depth of insertion of transpedicular vertebral screws into human vertebrae: effect upon screw-vertebra interface strength. J Spinal Disord. 1988; 1(4):287-294.[26]Bambakidis NC, Feiz-Erfan I, Horn EM, et al. Biomechanical comparison of occipitoatlantal screw fixation techniques. J Neurosurg Spine. 2008;8(2):143-152. [27]Okuyama K, Sato K, Abe E, et al. Stability of transpedicle screwing for the osteoporotic spine. An in vitro study of the mechanical stability. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(15): 2240-2245.[28]殷渠东,郑祖根,蔡建平,等.置入胸椎“椎弓根-肋骨”单元螺钉的应用解剖和力学测试[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2005,23(5):538- 539.[29]唐祀衡,陈建海,姜保国,等.椎弓根螺钉把持椎弓根皮质骨对其固定强度的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2005,15(7):429-432.[30]Weinstein JN, Spratt KF, Spengler D, et al. Spinal pedicle fixation: reliability and validity of roentgenogram-based assessment and surgical factors on successful screw placement. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1988;13(9):1012-1018.[31]Hirano T, Hasegawa K, Takahashi HE, et al. Structural characteristics of the pedicle and its role in screw stability. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997;22(21):2504-2510.[32]Brantley AG, Mayfield JK, Koeneman JB, et al. The effects of pedicle screw fit. An in vitro study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994;19(15):1752-1758.[33]董献成,荆鑫,张明建,等.胸椎椎弓根螺钉固定失败经椎弓根外入路补救的力学测试[J].临床骨科杂志,2008,11(6):564-566. |
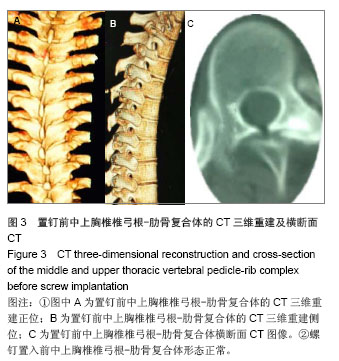
.jpg)
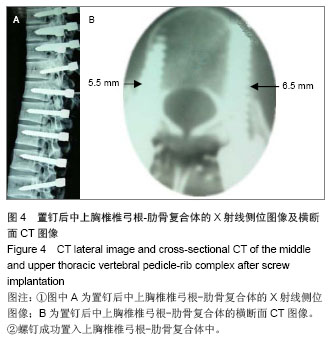
.jpg)
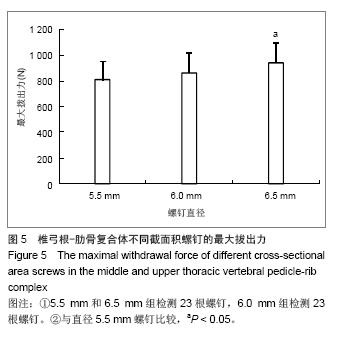
.jpg)